
Qiao's Pathology Sclerosing Adenosis with Perineural Inva… Flickr
On histology, sclerosing adenosis, as the name indicates, comprises lobules expanded by proliferated acini (adenosis) with, in addition, a variable amount of intervening stromal sclerosis that may result in compression and distortion of the acinar structures.

Pathology Outlines Sclerosing adenosis
As a subtype of adenosis, sclerosing adenosis (SA) is a benign proliferative disease of the breast associated with disordered acinar, myoepithelial and connective tissue in the terminal ductal lobular unit.

Sclerosing Adenosis of the Breast Pathology mini tutorial YouTube
The first one is sclerosing adenosis, which is the subtype characterized by calcifications and proliferation of small ductules and acini in the lobules. The second one is epithelial hyperplasia of cells in terminal ducts and lobular epithelium, which is associated with an increased risk of breast cancer only if there's a presence of atypical.
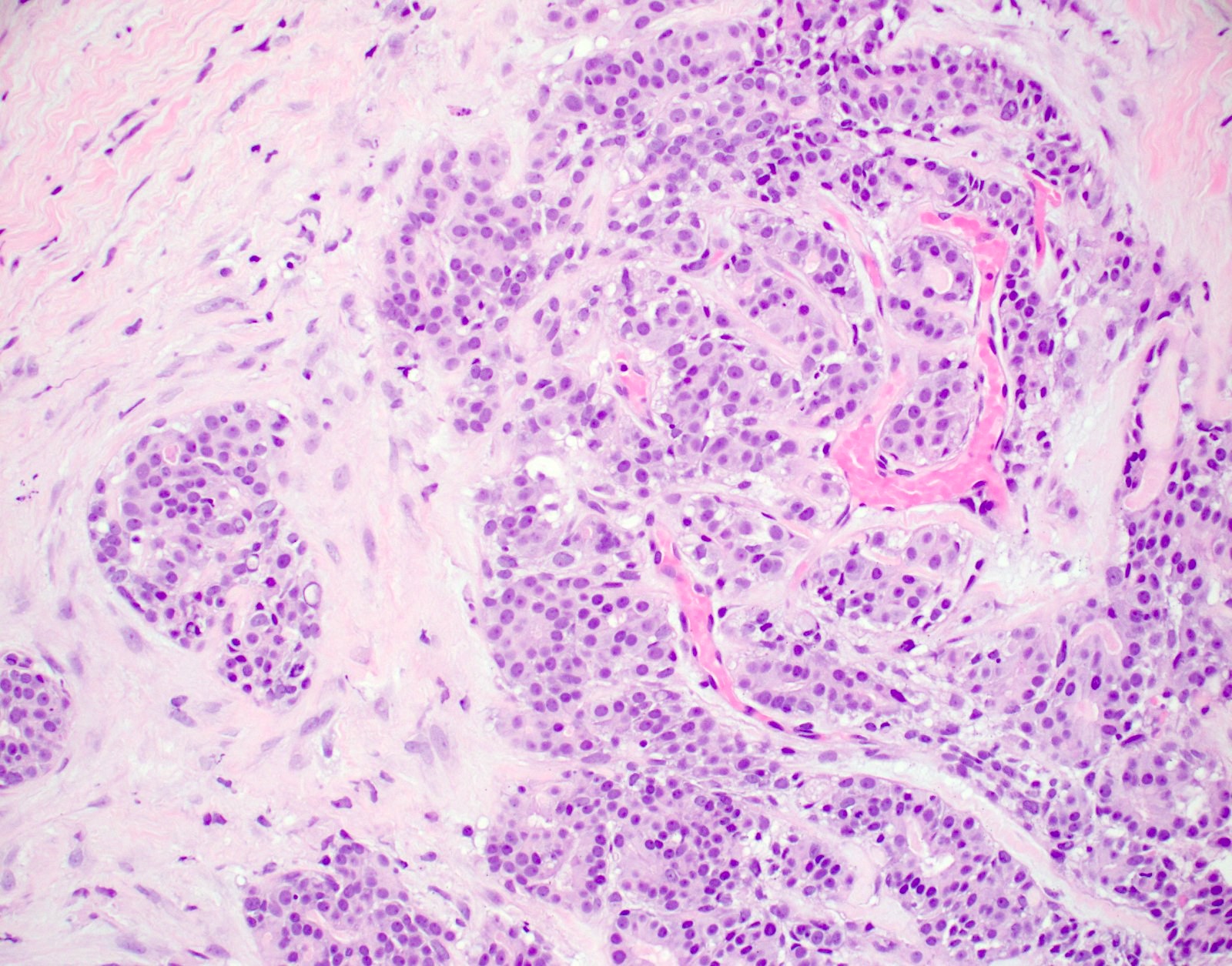
Pathology Outlines Adenomyoepithelial adenosis
Sclerosing adenosis proved to be a minor component at core biopsy for 44 lesions, including one invasive ductal carcinoma, one ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS), one focus of atypical ductal hyperplasia (ADH), and one atypical lobular hyperplasia.

Qiao's Pathology Sclerosing Adenosis with Associated Calc… Flickr
Essential features Proliferation of glands, typically lobulocentric (expanding terminal duct lobular unit) Terminology Simple adenosis Special subtypes: Adenomyoepithelial adenosis Apocrine adenosis Sclerosing adenosis Tubular adenosis (tubular adenoma) Nodular adenosis / adenosis tumor Blunt duct adenosis (now classified as columnar cell change )

Pin on stain research
Sclerosing adenosis is a common lesion of the breast, most prevalent in women of reproductive or perimenopausal age, especially those in the third and fourth decades. It is present in over one quarter of all benign breast biopsies, frequently in association with other proliferative and nonproliferative fibrocystic changes [ 4 ].

Breast carcinoma in sclerosing adenosis a clinicopathological and
Sclerosing adenosis is a special type of adenosis in which the enlarged lobules are distorted by scar-like tissue. This type may cause breast pain. Diagnosis of breast adenosis If many enlarged lobules are close to one another, they may be large enough to be felt as a breast lump.
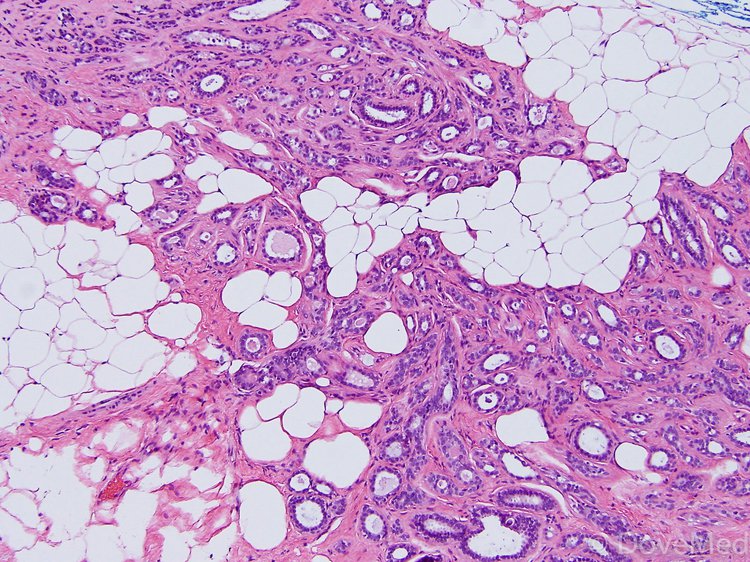
adenosis Liberal Dictionary
Sclerosing adenosis. 1989 Nov-Dec;13 (6):721-5. doi: 10.1007/BF01658421. The literature regarding sclerosing adenosis has been reviewed. The pathological and radiological aspects of this benign breast condition have been emphasized since they influence clinical practice. Features of 43 patients diagnosed as having sclerosing adenosis have been.
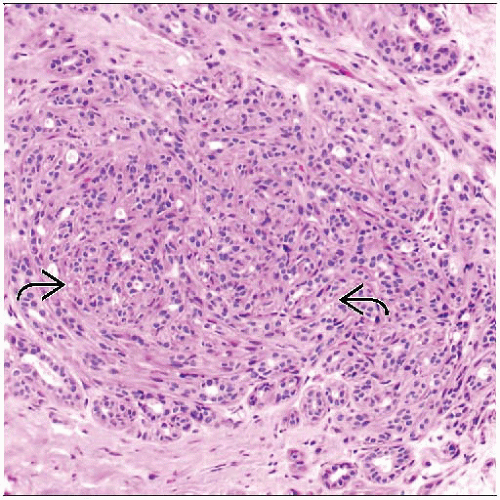
Sclerosing Adenosis Basicmedical Key
Epidemiology. Most common benign tumor of the female breast. Most common breast tumor in adolescent and young women. Can occur at any age, median age of 25 years ( J R Coll Surg Edinb 1988;33:16 ) Juvenile fibroadenoma generally occurs in younger and adolescent patients < 20 years; reported in children at a very young age ( Am J Surg Pathol.

Pathology Outlines Adenosis
Definition / general Rare salivary gland disorder, first described in 1996 ( Am J Surg Pathol 1996;20:161 ) Resembles fibrocystic changes and sclerosing adenosis of the breast ( Head Neck Pathol 2020;14:630 ) Exact nature of the disease is unknown but recent evidence suggests that it is neoplastic ( Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:e33 ) Essential features

Pathology Outlines Sclerosing adenosis
Sclerosing adenosis of the breast, also sclerosing adenosis, a benign pathology of the breast associated with an increased risk of malignancy. Contents 1 General 2 Microscopic 2.1 Images 3 See also 4 References General Can look like ductal carcinoma. Derived from sclerosing [1] (hardening) and adenosis (glandular proliferation).
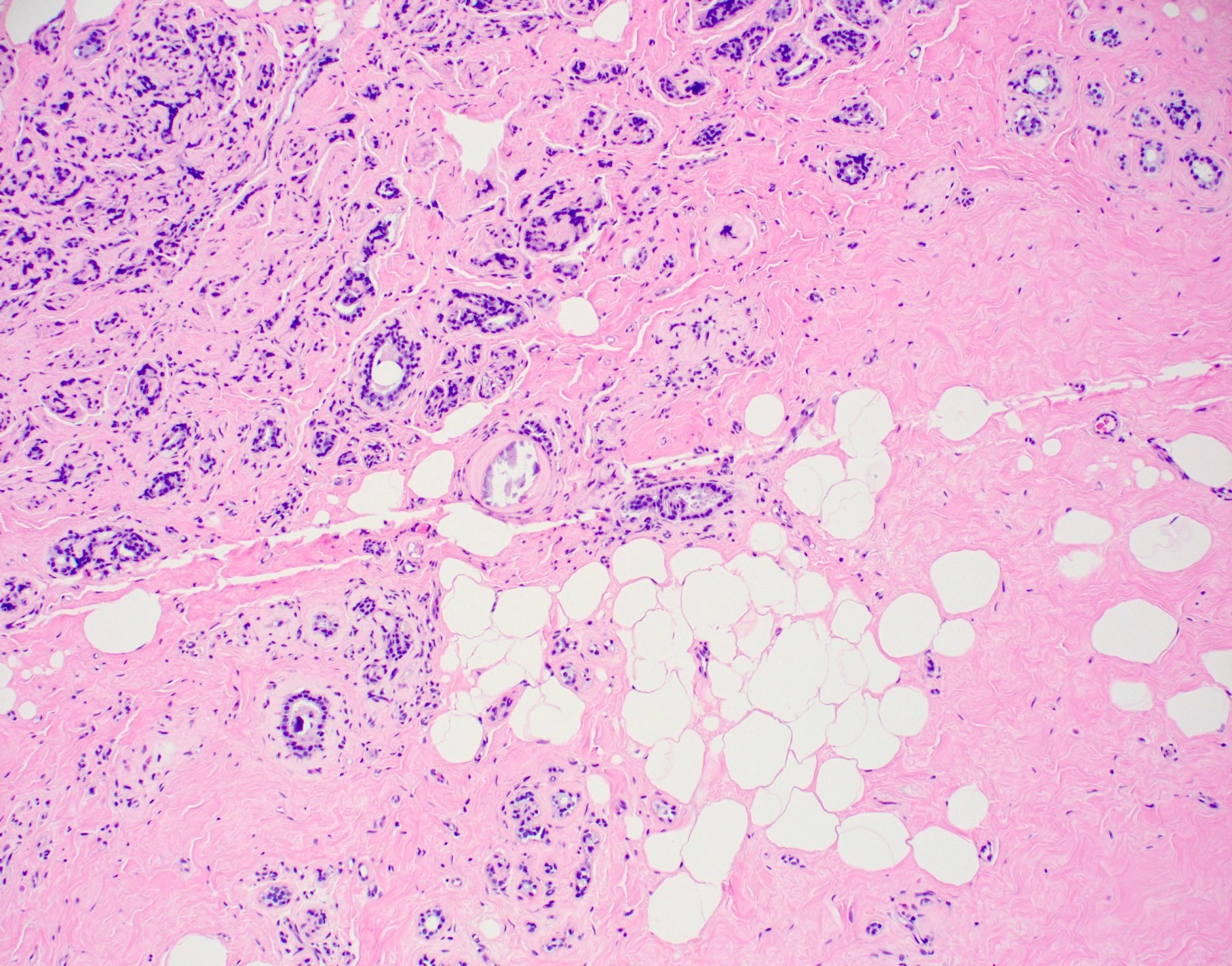
Pathology Outlines Sclerosing adenosis
Duct ectasia. Columnar alteration with prominent apical snouts and secretions (CAPSS) Papillomatosis. Fibrocystic changes. All of these are benign (non-cancerous) changes that the pathologist might see. These conditions generally do not need to be treated unless they're causing bothersome symptoms.
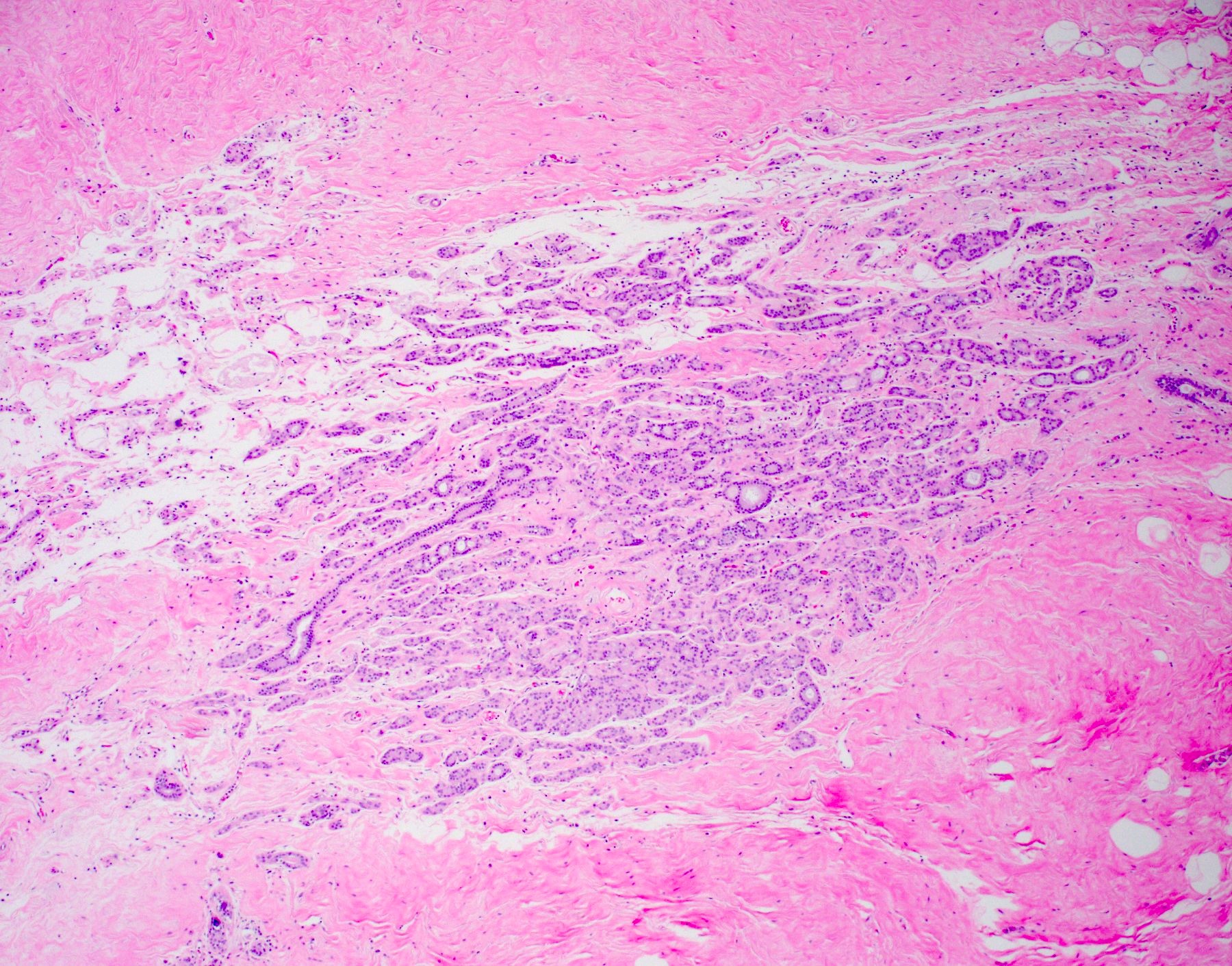
Pathology Outlines Sclerosing adenosis
SA is a lobulocentric proliferation of distorted acini around a central duct with preservation of myoepithelial cells, accompanied with varying degrees of epithelial atrophy and stromal fibrosis. Clinical Features Incidence SA is often an incidental finding in breast tissue removed for other reasons.
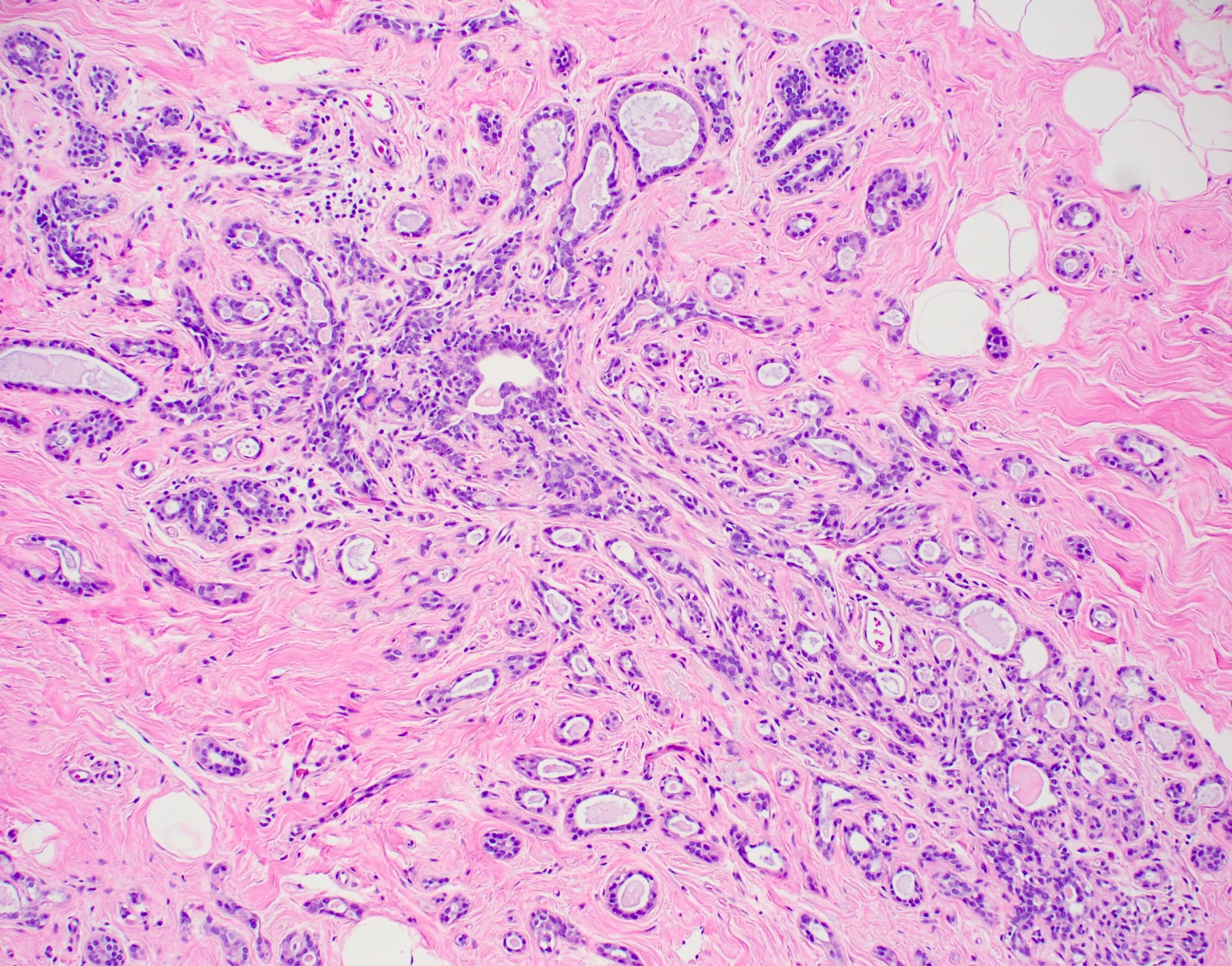
Pathology Outlines Sclerosing adenosis
Definition / general Adenosis or lobulocentric processes with increase in glandular elements of terminal duct lobular unit (TDLU) with stromal fibrosis / sclerosis that distorts and compresses glands Preserved 2 cell layer (inner epithelial and outer myoepithelial cells) Essential features
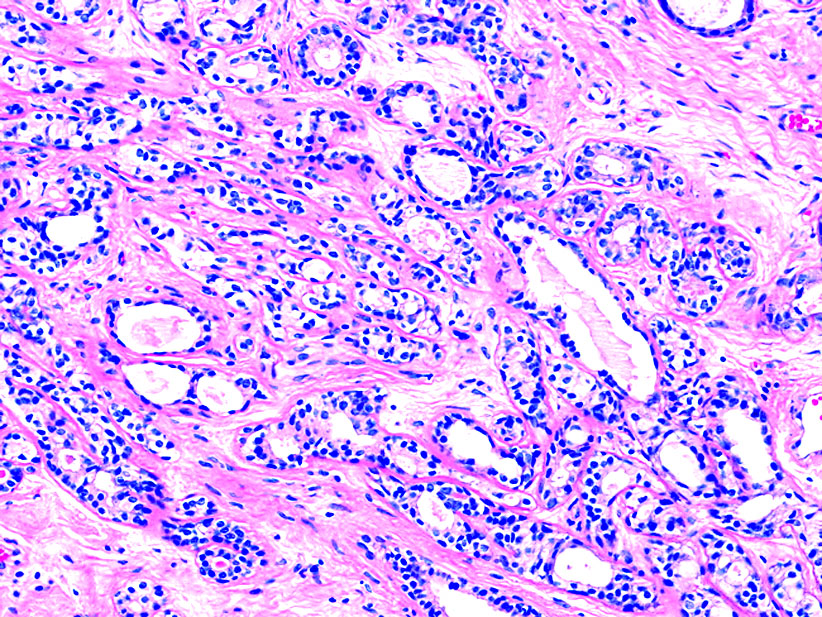
Pathology Outlines Adenosis
Sclerosing adenosis is a benign, usually asymptomatic lobulocentric proliferative process that involves both the epithelial and the mesenchymal component of the breast. It is commonly an incidental finding in perimenopausal women undergoing screening mammography. Case Report

Pathology Outlines Sclerosing adenosis
Sclerosing adenosis is a type of adenosis in which enlarged acini become slightly distorted by surrounded stromal fibrosis ("sclerosis"). The normal lobular architecture of the breast is maintained but becomes exaggerated and distorted. Radiographic features Mammography